How Would You Explain the Different Theories of Forgetting
It is learnt that the memory traces are responsible for our memory. An association takes time to set.

Why Do We Forget Forgetting Theories Of Forgetting In English Language By Dear Knowledge Youtube
Forgetting is the inability to recall or recognise information that was once stored in the memory and is now not available or cannot be accessed.

. To get full document. Theories of forgetting. Theories of Forgetting is a novel made up of three intersecting narratives.
The first involves the story of a middle-aged video artist Alana working on a short experimental video about Robert Smithsons land art Spiral JettyThe second involves the story of Alanas husband Hugh and his slow disappearance throughout Europe and across Jordan on a trip there both to. The concern about the causes of forgetting as to how and why it happens has led to extensive research and development of some theories. Under interference theory all memories interfere with the ability to recall other memories.
There are many theories to consider which explain why forgetting. I There is a phenomenon of retroactive inhibition in connection with the formation of associations. The trace decay theory of forgetting states that all memories fade automatically as a function of time.
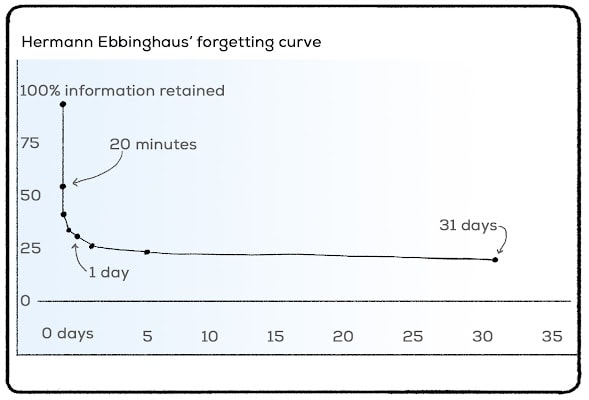
This could be due to the fact one does not want to pay attention. Information in short-term memory lasts several seconds and if it is not rehearsed the neurochemical memory trace quickly fades. Various theorists including Ebbinghaus 1885 1913 have argued that forgetting occurs because there is spontaneous decay of memory traces over time.
Trace decay cue dependant displacement and interference. There are a few different ways and reasons that we forget things. Click again to see term.
Forgetting is the inability to recall or recognise information that was once stored in the memory and is now not available or cannot be accessed. Trace theory proposes that the length of. These theories plus descriptions of aging studies that relate to them constitute the text of the present chapter.
As youve come to see memory is fragile and forgetting can be frustrating and even embarrassing. According to Drever 1952 Forgetting means failure at any time To recall an experience when attempting to do so or to perform an Action previously learnt. Learn more about why you forget and some things you can do to improve your memory.
Forgetting information happens usually in the first. The process of locating and recovering stored information from memory so that we are consciously aware of it. When forgetting in long-term memory arises from a strong motive or desire to forget usually because the experience is too disturbing or upsetting to remember.
Ive a grand memory for forgetting quipped Robert Louis Stevenson. Forgetting refers to loss of information from long-term memory. Memory or forgetting labels a diverse set of cognitive capacities by which we retain information and reconstruct past experiences usually for present purposes.
When you forget something it means that it is unavailable to you at the time you are trying to remember it not that it is gone forever. According to this theory a memory trace is created every time a new theory is formed. There are many reasons as to why one forgets things.
If a bond of association between A and B is formed and just after this a bond between C and D is formed then the formation of the latter tends to inhibit the former. The Trace Decay Theory. Displacement seeks to explain forgetting in the short.
Some of the important theories are. There are at least three general categories of theories of memory which suggest reasons why we forget. Forgetting refers to the inability to retrieve previously stored information.
Decay theory suggests that. The information may be stored in your memory but for some reason you cannot retrieve it when you want. Memory is processed and stored in a physical form but degrade over time particularly if they are unused leading to forgetting.
Proactive interference occurs when memories from someones past. Memory is one of the most important ways by which our histories animate our current actions and experiences. There are four main theories to forgetting.
There are four main theories to forgetting. The theories can be classified as psychological neurochemical and physiological. Click card to see definition.
Inference theory- when you partially remember but not fully. The tendency for one memory to interfere with the accurate retrieval. Trace decay cue dependant displacement and interference.
There are two types of interference proactive and. The Theories Of Forgetting. The decay theory- when someone has short term memory and stimulus is too weak to hold onto information displacement theory- when you also have short term memory but this is because too much information is received at a fast pace and you cant hold onto it all.
Most notably the human ability to conjure up. These traces are also called as engrams. Forgetting is a normal part of life but it can sometimes cause problems.
Under this theory you need to follow a certain path or trace to recall a memory. Tap again to see term. When used in the study of forgetting it refers to.
Tap card to see definition. Displacement seeks to explain forgetting in the short term memory. To get full document.
One does not encode the information into ones short term memory and rehearse it long enough to stay in the long term or it could be that one does not wish want to remember it. Trace decay cue dependant displacement and interference. Occurs one of them being interference- When something gets in the way.
We all forget things like a loved ones birthday someones name or where we put our car keys. 8 According to the trace decay theory of forgetting the events that happen between the formation of a memory and the recall of the memory have no impact on recall. Displacement seeks to explain forgetting in the short term memory.
Trace decay theory. According to Munn 1967 Forgetting is the loss temporary or Permanent of the ability to recall or recognize something learnt Earlier. The main assumption is that forgetting depends crucially on the length of the retention interval rather than on what happens during the time between learning and test.
Forgetting is the inability to recall or recognise information that was once stored in the memory and is now not available or cannot be accessed. Cue-dependent theory is criticised because memories can generalise over time their elements becoming less specific. There are four main theories to forgetting.
Five Theories Of Forgetting Memory Practical Psychology

1 Theories Of Forgetting 02 11 15

Theories Of Forgetting Manipulation Of Memory Ppt Video Online Download

No comments for "How Would You Explain the Different Theories of Forgetting"
Post a Comment